Egypt’s net international reserves climbed to $49.251 billion in August 2025, compared to $49.036 billion recorded at the end of July, representing an increase of $215 million, according to figures released by the Central Bank of Egypt (CBE).
The latest development follows April 2025’s milestone, when the country’s foreign currency reserves exceeded the $48 billion threshold for the first time in its history. This marks steady progress in Egypt’s efforts to stabilise its external position while pursuing broader economic reforms.
Egypt’s reserves consist of a diversified basket of global currencies, including the U.S. dollar, euro, British pound, Japanese yen, and Chinese yuan. The Central Bank periodically adjusts the allocation ratios of these currencies in response to global market conditions and exchange rate shifts, ensuring a flexible approach that shields the economy from volatility.
Earlier this month, President Abdel Fattah El-Sisi emphasised the importance of boosting foreign currency inflows from domestic resources while maintaining close coordination between government institutions and the CBE. His directives included sustaining a unified and flexible exchange rate regime to safeguard financial stability and support investor confidence.
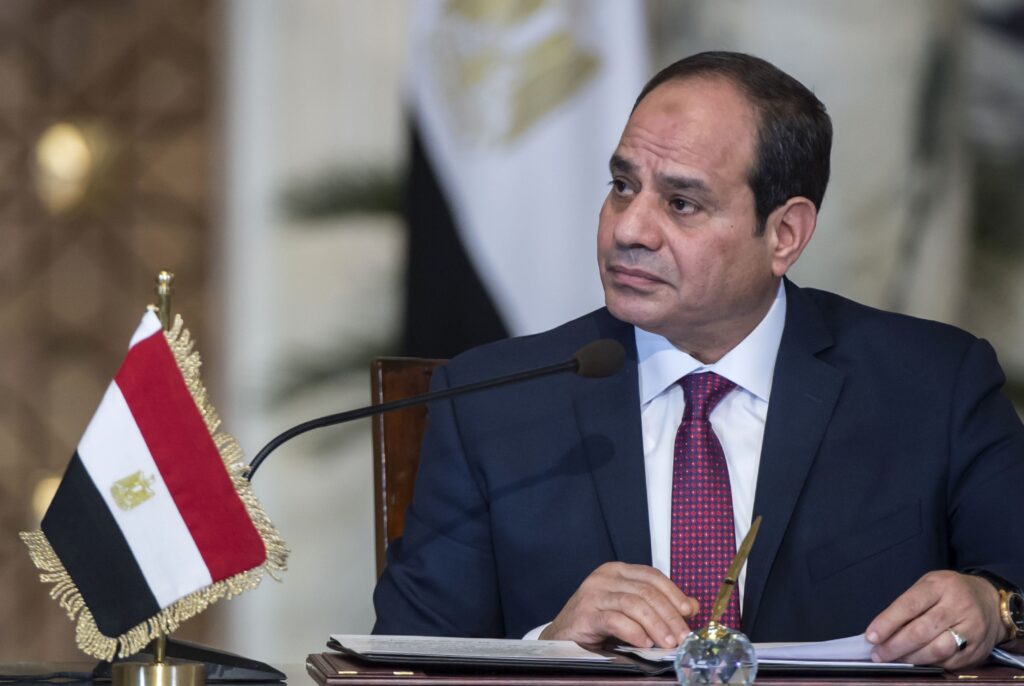

During a meeting with Hassan Abdullah, Governor of the CBE, El-Sisi reviewed economic indicators, including inflation control measures and policies aimed at further strengthening foreign exchange reserves. The President’s directives reflect a continuing drive to consolidate the country’s resilience in the face of regional and global economic pressures.
Government Targets Stronger Private Sector Role
Egypt has intensified efforts to reshape its economy, implementing nearly 500 reform measures since May 2022. These reforms focus on six key areas: monetary and exchange rate adjustments, enhancing competition, industrial sector support, improving the investment climate, legal and regulatory updates, and promoting private sector-led growth.
Officials say the overarching vision is to empower the private sector as a central engine of expansion, increasing its contribution to GDP, job creation, and export performance. Roughly two-thirds of the reforms so far have concentrated on creating a more favourable business environment and boosting investment opportunities.
In 2024, the government rolled out several initiatives designed to ease industrial operations, extend port activity to seven days a week, and broaden credit access for businesses in agriculture and manufacturing. These steps have already borne fruit, leading to more than $5 billion in new project contracts and a 14% rise in exports, which climbed to $40.8 billion.
Monetary policy has also undergone a shift, with the CBE adopting an inflation-targeting framework aimed at reducing inflation to 7% by 2026. This approach has strengthened Egypt’s investment climate and attracted $46.1 billion in foreign direct investment in the 2023/2024 fiscal year, underscoring growing global confidence in the country’s reforms.
Looking ahead, Egypt’s fiscal 2025/26 economic plan is designed to achieve a 4.5% growth rate, supported by public investments worth EGP 1.16 trillion and projected private sector contributions nearing EGP 1.94 trillion. The government has also stressed the need to rationalise public spending, reduce debt burdens, and encourage greater private participation in national projects.
At the same time, authorities are mindful of ongoing regional instability and international market disruptions. Policy adjustments, fiscal discipline, and reforms are being deployed to ensure that progress is not derailed by external shocks.
These concerted measures, analysts suggest, are shaping a pathway toward sustainable recovery and long-term resilience. Egypt’s record-breaking reserves and wide-ranging reforms reflect a determined push by policymakers to secure stability and growth in a challenging global environment.
READ ALSO: Chief Justice Removal Triggers Question On Judicial Indepence, Impunity