While global economic projections often dominate headlines, a closer look at individual countries reveals a complex picture of growth prospects and challenges. In the case of Ghana, the latest forecast from Standard Bank paints a promising picture, signaling that Ghana may be on the right path towards sustained economic prosperity.
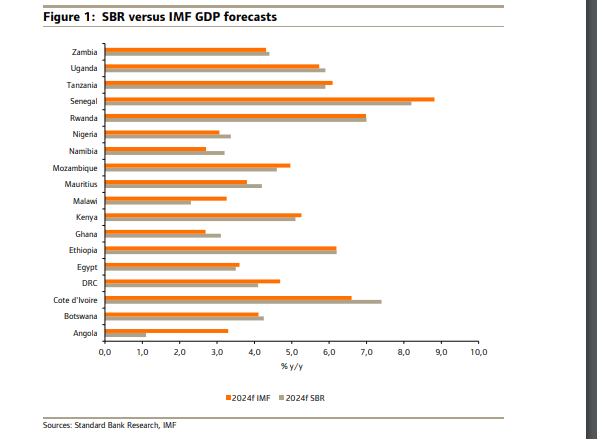
Standard Bank’s projection of a 3.2% growth rate for Ghana in 2024 surpasses the IMF’s earlier forecast of 2.8%, underscoring the country’s resilience and potential for robust economic expansion. This optimistic outlook bodes well for Ghana’s development agenda, as it strives to overcome challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Ghana’s growth story is anchored by the services sector, which is expected to be the primary driver of economic expansion this year. However, amidst this optimism, risks loom large. Factors such as El Niño weather patterns, mounting debt burdens, and geopolitical uncertainties could potentially impede Ghana’s growth trajectory.
The impact of unfavorable weather conditions on agricultural productivity, coupled with challenges in debt management, poses significant threats to the country’s fiscal stability. Additionally, geopolitical tensions both regionally and globally could introduce further volatility, impacting investor confidence and economic activities.
Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort to diversify the economy, strengthen fiscal management, and promote sustainable development practices. Ghana must prioritize investment in critical sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, and technology to foster inclusive growth and reduce dependency on external factors.
Historically, Ghana has showcased resilience, with consistent year-on-year growth averaging 5% until the emergence of the Covid-19 pandemic in 2019. However, navigating the aftermath of the pandemic and addressing structural challenges will be imperative for sustaining this growth momentum.
A Modest Expansion of the Economy
Data from the Ghana Statistical Service indicates a modest expansion of the economy, driven primarily by the services and agriculture sectors. Despite this growth, there remains a noticeable slowdown compared to previous years, highlighting the need for targeted interventions to stimulate economic activity.
While Ghana’s growth prospects are promising, it is essential to contextualize them within the broader African context. Ethiopia, for instance, is poised to record the highest growth rate in Africa, nearing an impressive 10% in 2024. This underscores the diversity of growth trajectories across the continent and the unique challenges each country faces.
The IMF anticipates a rebound in GDP growth for Sub-Saharan Africa, projecting a growth rate of around 4.0% in 2024. However, achieving this growth will require concerted efforts to address underlying vulnerabilities and foster a conducive environment for sustainable development.
As Ghana strives to capitalize on its projected growth in 2024, it must concurrently address the inherent risks that threaten to undermine its economic trajectory.
Ghana’s heavy reliance on the services sector for growth underscores the need for diversification. By promoting investment in sectors such as manufacturing, technology, and renewable energy, Ghana can reduce its vulnerability to external shocks and foster long-term resilience.
In addition, mounting debt burdens pose a significant threat to Ghana’s fiscal stability. Implementing prudent debt management practices, enhancing revenue mobilization efforts, and promoting fiscal discipline are essential to mitigate the risks associated with high levels of indebtedness.
As Ghana charts its course for 2024 and beyond, it must remain committed to implementing bold reforms, fostering inclusive development, and building resilience to external shocks. By harnessing its rich resources, human capital, and entrepreneurial spirit, Ghana can overcome challenges, exceed expectations, and pave the way for a prosperous future.




















