Cashew farmers are voicing serious concerns over obstacles that are impeding their ability to fully capitalize on the cashew crop.
These challenges, as highlighted by the farmers, include a lack of knowledge and resources to enhance the value of cashew apples, market instability, and limited access to agricultural funding. This also includes increasing costs of farm inputs, and an unfavorable land ownership system, among other issues.
The farmers describe feeling “helpless” as these problems persist with little action from authorities to resolve them and enhance the sustainability of cashew farming as a livelihood.
In an interview, Eric Nyamekye, a 62-year-old farmer who owns 70 acres of cashew farms in Nsawkaw, Tain District of the Bono Region, shared his struggles with the poor economic returns from his cashew apples.
“I have been cultivating cashews since 1986, but every passing production season is frustrating with the wasted potential of the cashew apples, which make over 80 percent of the crop weight. There are no processing facilities and resources for farmers to transform the nutritious fruit into value-added products.”
Eric Nyamekye
Research indicates that cashew apples hold the potential for processing into valuable products like juice, jams, and wine, a practice that has notably increased farmers’ earnings and food security in countries like Brazil.
Furthermore, The global market for cashew apples is dynamic and its value varies depending on region and market demand. As of 2024, Canada leads in cashew apple exports with a value of $491.6 million, representing a 20.41% market share.
Malaysia follows with $289.2 million (12.01%), and Poland with $287.2 million (11.93%). Chile and the United States also contribute significantly with export values of $224.6 million (9.33%) and $199.4 million (8.28%) respectively.
These export figures highlight the substantial role of cashew apples in the global market. Wholesale prices for cashew apples can also fluctuate, with reports showing prices ranging from $10.48 to $13.68 per kilogram as of May 2024.
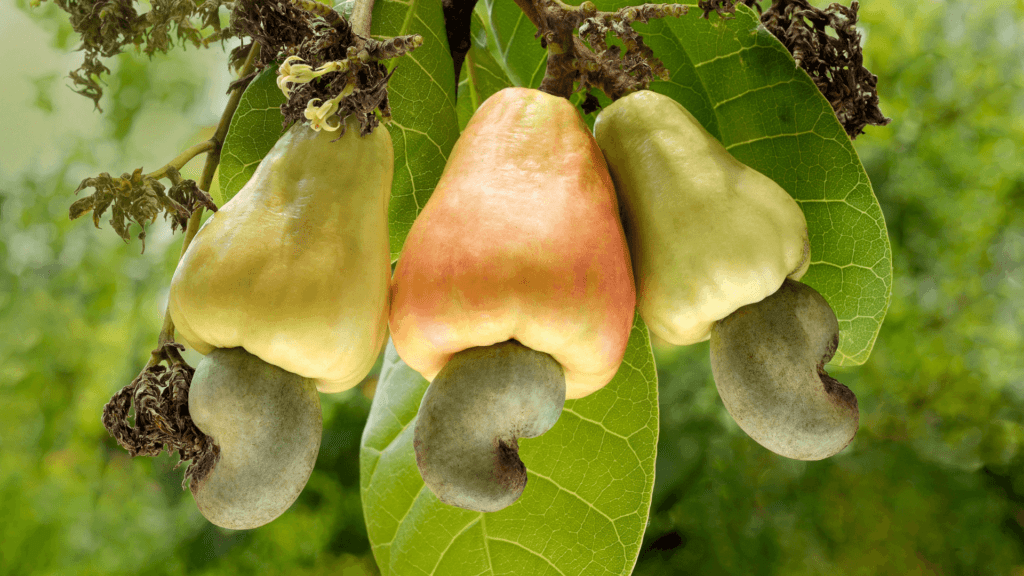
In Ghana, however, farmers such as Mr. Nyamekye primarily depend on selling raw cashew nuts, which do not adequately offset rising production expenses, including labor and inputs like pesticides.
“This underscores the need for interventions to support cashew farmers in Ghana to explore value-added processing opportunities and enhance our livelihoods,” he added.
Also, James Wayi, a 29-year-old cashew farmer from Anukurano near Drobo in the Jaman-South Municipality of the Bono Region encounters difficulties in obtaining affordable agricultural credit.
This obstacle prevents him from expanding his cashew plantations, which in turn limits the potential for boosting production and fostering economic growth in the region.
Strategic Measures to Empower Cashew Farmers
To address the challenges faced by cashew farmers in Ghana, the government should consider implementing these strategic interventions.
Firstly, there is a critical need for investment in farmer education and resources aimed at enhancing the value of cashew apples through processing.
Establishing processing facilities and providing training on value-added product development, such as juice and jams, can unlock new income streams for farmers like Eric Nyamekye.
Moreover, the government should prioritize stabilizing the market environment to ensure consistent and fair prices for cashew products.
Additionally, to tackle the issue of limited access to agricultural financing, the government could work with financial institutions to develop tailored credit schemes with affordable interest rates for cashew farmers.
This would enable farmers like James Wayi to expand their operations and invest in productivity-enhancing inputs without financial constraints.
Furthermore, addressing the challenges around land ownership and tenure is essential. The government should streamline land tenure policies to provide secure land rights for farmers, encouraging long-term investment and sustainable agricultural practices.
By implementing these targeted measures, the government can empower cashew farmers, promote value addition, improve market stability, and facilitate access to essential resources and financing in Ghana.
READ ALSO: Government Prioritizes Creativity And Innovation In Education To Drive National Development





















